Triangles of the neck
A man presents with a pulsatile neck lump in the anterior triangle that moves with swallowing. Diagnosis?
- ((Branchial cyst::No movement, not pulsatile, typically lateral neck))
- ((Chemodectoma::Carotid body tumour; pulsatile but only moves side-to-side))
- [[Thyroid nodule::Midline anterior neck lump moving on swallowing suggests thyroid origin]]
- ((Lymphadenopathy::No movement, not pulsatile, may be tender))
Ludwig’s angina typically affects which deep neck space?
- [[Submandibular space::Ludwig’s angina is a rapidly spreading cellulitis of the submandibular, sublingual and submental spaces, usually from mandibular molar infections.]]
- ((Retropharyngeal space::Infections here cause midline posterior pharyngeal bulging and may descend into the mediastinum.))
- ((Pre-tracheal space::Involvement here leads to anterior neck swelling related to thyroid or tracheal structures.))
- ((Parapharyngeal space::Infections produce trismus, severe sore throat and cranial nerve complications.))
Ludwig’s angina is a bilateral cellulitis of the submandibular space of the anterior triangle, often due to infected lower molars. It is a rapidly spreading infection with risk of airway compromise and requires urgent airway assessment.
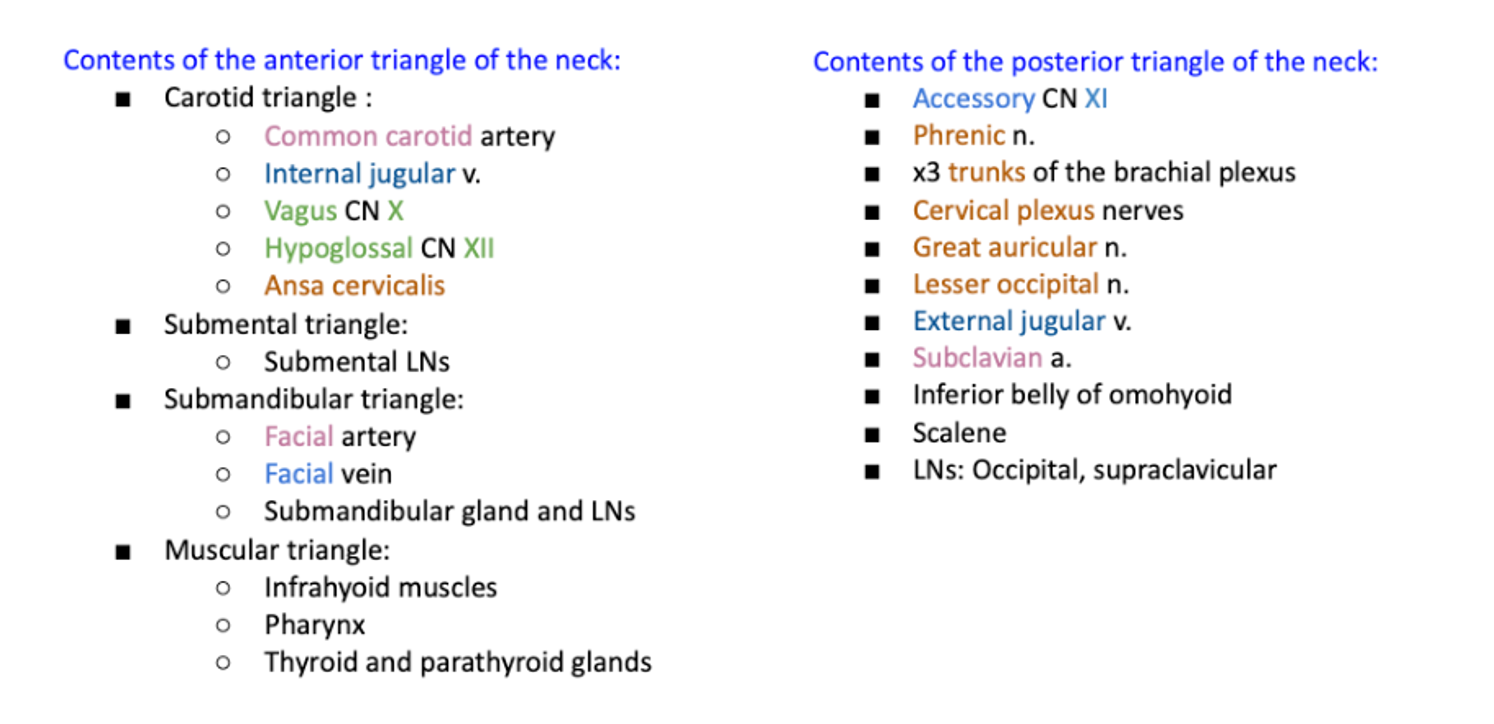
Contents of the submandibular triangle of the anterior triangle:
- Facial artery
- Facial vein
- Submandibular gland
- Submandibular lymph nodes
During a Level V neck dissection in the posterior triangle, which nerve is most at risk of injury?
Spinal accessory CN XI
The spinal accessory CN XI crosses the posterior triangle, running superficially and is highly vulnerable during lymph node biopsies or neck dissections. Injury can lead to trapezius muscle weakness, resulting in shoulder droop and difficulty in > 90° shoulder abduction. It is one of the most common iatrogenic nerve injuries in the neck.
💥 CN X is anterior, CN XI is posterior, CN XII is anterior.
A 19-year-old woman is shot in the neck with an airgun pellet. During surgical exploration of the posterior triangle, she becomes unable to elevate her left shoulder or fully abduct her left arm. Which structure was most likely injured?
- [[Accessory nerve (CN XI)::The spinal accessory nerve runs superficially through the posterior triangle and supplies the trapezius; injury causes shoulder droop and weak abduction above 90°.]]
- ((Phrenic nerve::Runs on the anterior scalene and supplies the diaphragm; injury causes breathing difficulties.))
- ((Long thoracic nerve::Supplies serratus anterior; injury causes winged scapula.))
- ((Dorsal scapular nerve::Supplies rhomboids and levator scapulae; injury weakens scapular retraction.))