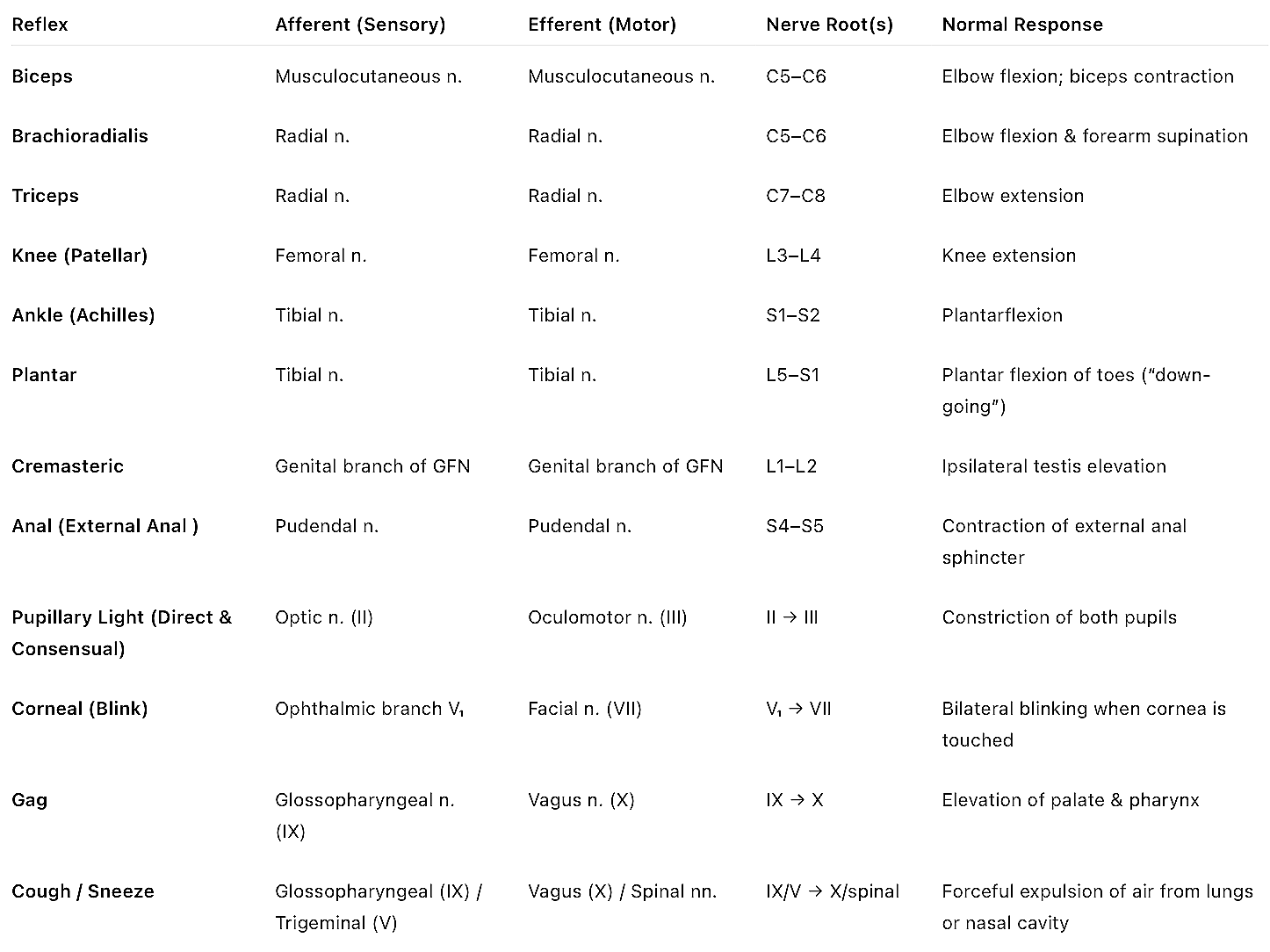
Reflex Arcs
Summary table of reflex arcs


Pupillary light reflex pathway
- Retina detects light
- Optic CN II
- Bilateral pretectal nucleus in midbrain
- Bilateral Edinger-Westphal nuclei
- Parasympathetic fibres of Oculomotor CN III
- Ciliary ganglion
- Short ciliary nerves
- Sphincter pupillae muscle
- Direct and consensual pupillary constriction
Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- is located in the midbrain
- provides preganglionic parasympathetic fibres that travel with the oculomotor CN III
- to innervate, via the ciliary ganglion, the:
- pupillary sphincter to enable pupillary constriction
- ciliary muscles for lens accommodation.
Edinger-Westphal nucleus ⏩ Oculomotor CN III ⏩ Ciliary ganglion ⏩ Short ciliary nerves ⏩ Pupillary sphincter and ciliary muscles
An Edinger-Westphal nucleus lesion causes an abnormally dilated pupil, and abolishes both direct and consensual light reflexes on the side of the lesion.
Lacrimal system
- Lacrimation reflex pathway:
Conjunctiva irritation → Lacrimal n. → Ophthalmic n. (V1) → Trigeminal sensory centre → Superior salivary nucleus → Facial CN VII → Greater petrosal n. → Pterygopalatine ganglion → Joins zygomatic branch of trigeminal’s maxillary CN V2 → Joins the lacrimal branch of V1 → Lacrimal apparatus
- Arterial supply to the lacrimal system is via a lacrimal branch of the ophthalmic artery of the internal carotid artery.
- Venous drainage is to the superior ophthalmic vein.
📚 Exam-style questions
- A patient presents with asymmetrical pupils and abnormal light reflex. Where is the lesion most likely?
- [[Edinger-Westphal nucleus::Midbrain nucleus for parasympathetic output for pupil constriction]]
- ((Hippocampus::Memory processing))
- ((Lateral geniculate body::Visual relay))
- ((Locus coeruleus::Noradrenergic, regulates arousal))
- ((Posterior limb of internal capsule::Motor fibres))
- What is the afferent limb of the gag reflex?
- [[Glossopharyngeal::In the gag reflex: Glossopharyngeal CN IX is the afferent limb; vagus CN X is the efferent limb]]
- Vagus
- Facial
- Temporal